What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. Although it can affect any joint, it most commonly impacts joints in the hands, knees, hips, and spine. Here are some key symptoms of osteoarthritis:
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Tenderness
- Swelling
Remember that while osteoarthritis symptoms can be managed, the damage to joints cannot be fully reversed. Staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and receiving appropriate treatments can help slow its progression and improve pain and joint function.
Risk Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis
Older Age
Gender
Obesity
Joint Injuries
Certain Occupations
Genetics
Bone Deformities
What are the stages of knee osteoarthritis
Stage 1: There is minor damage to the joint, with very minor bone spur growth. There is usually no pain or discomfort. .
Stage 2: The cartilage begins to show damage, with early symptoms of pain and stiffness after a period of inactivity. Small bone spurs develop.
Stage 3: The cartilage deteriorates further, with obvious erosion and a narrowing of the space between the bones. Symptoms worsen, with frequent pain and stiffness, especially after sitting for long periods or in the morning. Bone spurs are visible on an X-ray.
Stage 4: There is little to no cartilage in the knee, with pronounced bone spurs and severe pain. The joint space is dramatically reduced, and symptoms significantly interfere with daily life

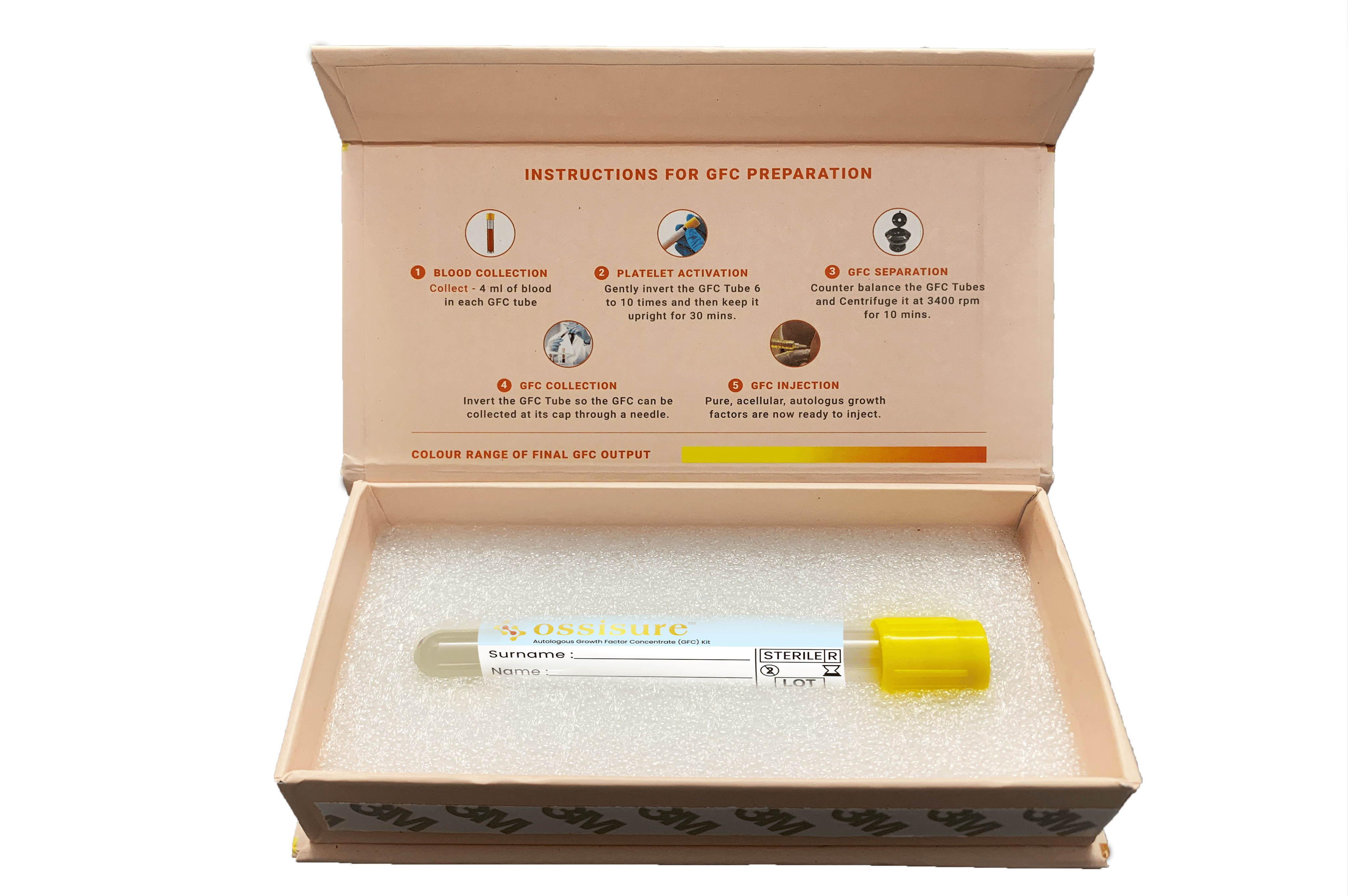
How to prepare GFC

Step 1 - Collection of Blood
Collect 4ml of Patient’s Peripheral blood in GFC tube

Step 2 - Activation of Platelet & Release of GFs
Gently mix the blood by inverting tube for 6-10 times & allow tube to stand for 30 mins (This activates platelets by Pattern’s proprietary Platelet Activating Solution present in tube and releases all GFs from Granules present in platelets).

Step 3 - Separation of GFC
Centrifuge GFC tube at 3400 rpm for 10 min. Tube should be counter balanced before centrifugation. This will separate pure GFs from rest of blood cells (like RBCs, WBCs etc.).

Step 4 - Collection of GFC
Invert tube to allow GFC to get collected at the cap of tube. To collect GFC, insert a needle of collecting syringe into the tube so that the tip of the needle is just under the cap to allow maximum recovery of GFC.

Step 5 - Application of GFC
GFC (about 2ml) thus collected is ready-to-use
Contact Us?
Address:
Kailash Tower, Vasai Link Road, Vasai Virar , Palghar, Maharashtra PIN 401209.
